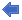
A 3D model is a set of connected 3D points, edges, curves and cylinders or shapes which represent an object. Three dimensional points have coordinate values for each of the Cartesian axes (X, Y, and Z).
The points and edges in the 3D model can be connected by lines and/or by patches, called Surfaces. These connections help the user to visualize the three dimensions when the model is projected onto a flat surface such as a computer monitor or a printed page.
This section provides an overview of the process of creating a 3D model with PhotoModeler, from start to finish.
There are eight steps to producing a model with PhotoModeler:
• Create a calibrated or approximate camera description,
• Plan the Measurement Project,
• Take photographs of the object or scene,
• Import the photographs into PhotoModeler,
• Mark features (e.g. points, shapes etc.) on the photographs,
• Identify which points are the same,
• Process the data, and
• Export the resulting 3D data to a CAD or graphics program.
The following sections describe each of the eight steps in greater detail.
The nature of the steps changes based on the type of project such as an automated SmartPoint project, an automated Coded Target project, a manual project, or a UAV / drone project. The basic theory and process is similar in all project types but some details are changed - based esp. on the level of automation. The following sections describe the overall theory and focus on manual projects mostly, and for additional detail on a specific project type visit one of the following sections: