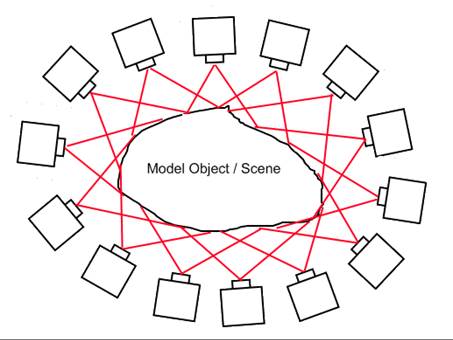
There are several settings to control how the MVS Cloud/Mesh is generated. In most cases, the default settings should produce a good DSM. However, there may be times when you will want to change the settings to improve or densify the result.
When you select a setting, the Help section below the settings briefly describes the selected setting. Below is a description of each setting.
Basic - Settings that may change with each new project:
• Min visible images - The minimum number of photos on which a feature must appear before it is considered to be a valid part of the point cloud. Lowering the value usually increases number of points, but may introduce more noise and less accurate points. This plays off density against noise and accuracy. 3 is usually a good default but in areas of poor overlap, you may require points on only 2 photos.
•
• Minimum angle - The minimum angle between two camera stations such that they are considered in supporting the reconstruction of a 3D point. A very low angle may result in noisy point clouds and a very high angle will produce sparse clouds. In degrees.
•
• Texture Strength - A threshold for the feature correlation ‘score’. If the feature correlation is lower than this threshold, a point will not be created. If the object has weak texture, use a lower value to increase point count at the expense of more noise.
•
• Down-sample level - The amount of image down-sampling. The higher the value, the more down-sampled is the image during feature detection. A value of 0 will use full resolution images and should produce most points. The lower this value the greater the number of points, the greater the detail, but the slower the processing time and potentially higher noise.
•
• Point Spacing - Controls the density of the resulting point cloud. A lower value increases density. For maximum density use 1.
•
Advanced - Advanced settings that in most projects can remain at default values:
•
• Max Group Size - The maximum number of photos grouped and processed simultaneously during stereo processing. Lowering this value reduces memory consumption but at the cost of fragmented groups of point clouds. Ideally, this parameter should be set as close to the total number of oriented photos in the project as memory allows.
•
• Window radius - The radius of the correlation area used in the search. Larger is slower with smoother results but may be useful if texture features are large. Smaller is faster but may be noisier.
•
• Number of iterations - Point cloud creation is an iterative process consisting of search and refinement stages. This parameter controls the total number of such iterations. A higher value produces denser and cleaner point clouds at the expense of computational time.
•
• Curvature Factor - This parameter controls the neighborhood of a 3D point. It is used in searching the 3D space for other points on the desired surface. When the desired surface is highly curved and/or very thin, a higher value >1.0 and <2.0 should be used.
•