Referencing:
|
Field |
Description |
|
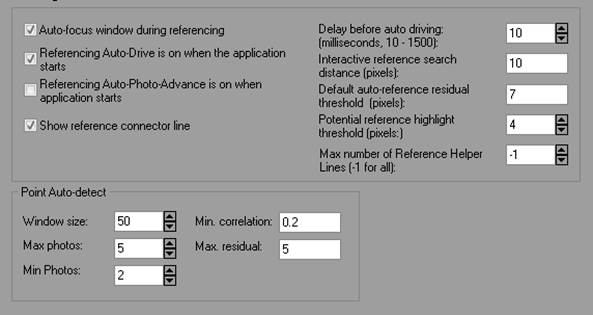
Auto-focus window during referencing |
If checked, the photo is automatically activated when the mouse moves over it while in referencing mode. |
|
Referencing Auto-Drive is on when the application starts |
If checked, the referencing auto-drive-to-point option is on for the first referencing. |
|
Referencing Auto-Photo-Advance is on when application starts |
If checked, the referencing auto-advance-to-next-photo option is on for the first referencing. |
|
Include coded points when automatic referencing |
If checked, coded points will be included when auto-referencing sub-pixel non-coded target points. |
|
Delay before auto driving (milliseconds, 10 - 1500) |
Controls how long a delay there is before referencing auto-drive takes place. |
|
Interactive Referencing search distance (pixels) |
Controls what distance is considered to be a valid matching point on a photo for weld. |
|
Default auto-reference residual threshold (pixels) |
The residual threshold used during auto-referencing. Potential references with a residual calculation less than this value will be accepted as a good referenced point. |
|
Potential reference highlight threshold (pixels) |
Controls the distance from the epipolar line that a candidate item for referencing will be highlighted during manual referencing. |
|
Max number of Reference helper lines (-1 for all) |
Controls the number of helper/epipolar lines that will appear while referencing. Select -1 (for all), 0 or 1. |
|
Point Auto-detect (see Point Auto-detect Mode) |
|
|
Window Size |
The size of the square window (pixels) used to traverse the epipolar line in potential images while detecting matching features. |
|
Max. Photos |
The maximum number of best photos on which matching features will be detected. Too high a number may cause processing delays without significant benefit. |
|
Min. Photos |
The minimum number of photos on which matching features will be detected. Too low a number may result in lower reliability points. |
|
Min Correlation |
The minimum correlation factor to deem a match valid. Decrease this value for more strict feature matching. |
|
Max Residual |
The points’ residual value is calculated as soon as a match is found. If the potential match’s residual is higher than this value, the match will not be marked. Decrease this value for more strict feature matching. |
Target Marking:
|
Field |
Description |
|
Automarking Automatic Segmentation Settings |
|
|
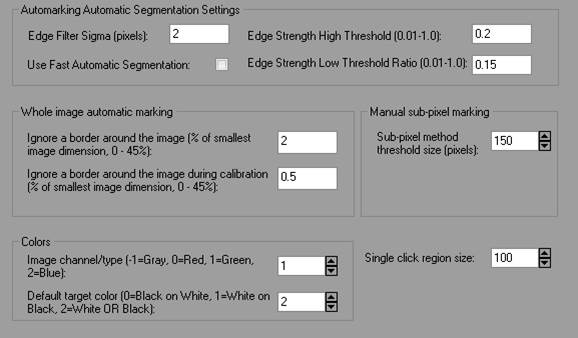
Edge Filter Sigma |
|
|
Use Fast Automatic Segmentation |
|
|
Edge Strength High Threshold |
|
|
Edge Strength Low Threshold Ratio |
|
|
Whole image automatic marking |
|
|
Whole image automatic marking |
|
|
Manual sub-pixel marking |
|
|
Sub-pixel method threshold size (pixels) |
|
|
Single click region size |
Controls the size of region surrounding the single click location for detection of a high contrast target during single click sub pixel target marking. Increase the size of region to detect very large dot targets or coded targets. |
|
Colors |
|
|
Image channel/type |
The image ‘channel’ to use when sub-pixel or automatic target marking. Marking in just one channel may improve marking precision because there will be less negative effects of chromatic aberration of the lens. Most digital cameras have more green sensors than red or blue and this is why the green channel is the default. |
|
Default target color |
When sub-pixel marking or automatic marking, PhotoModeler can detect whether targets are black on white or white on black. However, if you consistently use a certain type of target, you might want to switch to the applicable setting, which can improve marking speed. |
Coded Targets:
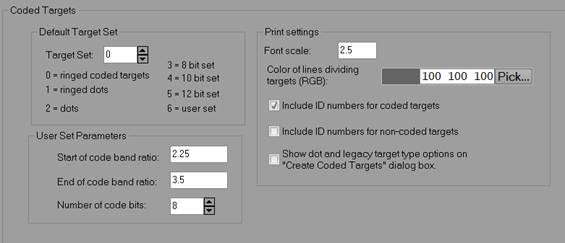
|
Field |
Description |
|
Default Target Set |
|
|
Target Set |
Determines the default set of targets used when setting up a project. 0 - RAD Targets, 1 – Ringed dots, 2 – plain dots, 3 – 8bit, 4 – 10bit, 5 – 12bit, 6 – user set. |
|
User Set Parameters |
|
|
Start of code band ratio |
If set #6 is chosen as the target set, the user can enter in the code ring start band ratio. |
|
End of code band ratio |
If set #6 is chosen as the target set, the user can enter in the code ring end band ratio. |
|
Number of code bits |
If set #6 is chosen as the target set, the user can enter in the number of bits in the code. |
|
Print Settings |
|
|
Font scale |
Controls the size of the ID next to the targets when printing coded targets. See Create Coded Targets Dialog. |
|
Color of lines dividing targets |
Controls the color of dividing lines between targets when printing targets. |
|
Include ID numbers for coded targets |
Includes the ID of the target to the lower left when printing |
|
Include ID numbers for non -coded targets |
Includes an ID to the lower left of the target, which though it may not correspond to the object point ID once marked and referenced, it can help identify a point when manually referencing the target. |
|
Show legacy target type options on “Create Coded Targets Dialog” |
Show options to print non-RAD coded targets (e.g. 8bit, 12 bit etc.). See Create Coded Targets Dialog. |
|
|
|